Nemesis11
Power Member
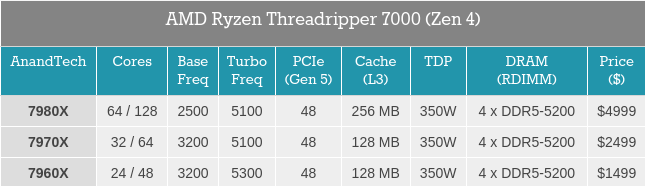
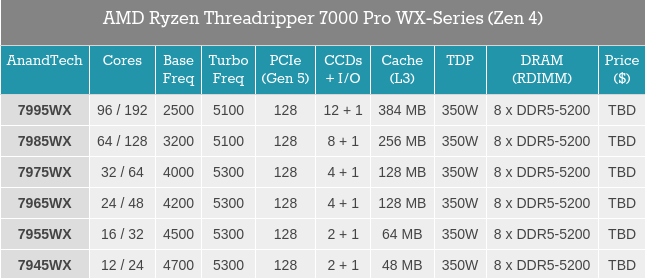
Alegadamente, specs do Threadripper Zen4.


https://wccftech.com/amd-ryzen-thre...ecs-leak-7995wx-flagship-96-cores-5-ghz-350w/
Não percebo a existência daquele SKU de 12 Cores, existindo um SKU com 16 Cores, praticamente com os mesmos Clocks.
Algo curioso é "só" suportar 8 canais de memória, ao contrário dos 12 do Epyc 9XXX e só o SKU com 96 Cores suportar 128 Lanes Pci-Ex, sendo que os restantes só suporta metade.
Todos os modelos com 350W TDP.
Lançamento dia 19 de Outubro.


https://wccftech.com/amd-ryzen-thre...ecs-leak-7995wx-flagship-96-cores-5-ghz-350w/
Não percebo a existência daquele SKU de 12 Cores, existindo um SKU com 16 Cores, praticamente com os mesmos Clocks.
Algo curioso é "só" suportar 8 canais de memória, ao contrário dos 12 do Epyc 9XXX e só o SKU com 96 Cores suportar 128 Lanes Pci-Ex, sendo que os restantes só suporta metade.
Todos os modelos com 350W TDP.
Lançamento dia 19 de Outubro.